Starter Manual: No Load Test Guidelines
Product Overview
This comprehensive manual provides detailed instructions for conducting no load tests on starter systems. It helps diagnose common problems that can affect performance, assisting engineers and technicians in maintaining optimal functionality of starters in heavy machinery.
Key Features
- Step-by-step troubleshooting guide for starter systems
- Includes procedures for testing armature and field coils
- Covers inspection of key components like bearings and commutator bars
Benefits
- Improve machinery reliability by ensuring proper starter function
- Reduce downtime through efficient diagnostics
- Enhance safety by identifying potential electrical faults
Usage Recommendations
- Use the manual to guide diagnosis if starter operation issues arise.
- Refer to the specified pages for detailed testing procedures of armature and field coils.
- Pair with the appropriate tools, such as an armature tester, as recommended in the instructions.
Troubleshooting Overview
Understanding no load test results is crucial for determining starter health:
-
1. Normal Operation:
If the current draw and armature shaft speed are within specifications, the starter is functioning correctly.
-
2. High Current Draw, Low Shaft Speed:
Indicative of excess friction due to:
- Dirty or worn bearings.
- Bent armature shaft.
- Loose pole shoes contacting the armature.
- Short circuit in the armature coil. Use an armature tester.
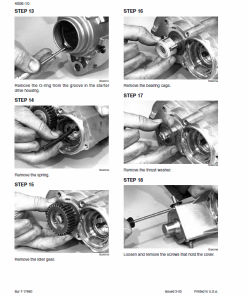
- Damaged field coil. See tests on page 4006-12.
-
3. High Current Draw, No Shaft Rotation:
Potential causes include:
- Field terminal contact issues. Inspect insulators carefully.
- Damaged field coil. Refer to page 4006-13 for tests.
- Damaged bearings.
-
4. Zero Current Draw, No Shaft Rotation:
Possible reasons are:
- Open field circuit. Inspect connections.
- Open armature coil. Look for burned commutator bars.
- Poor brush contact with commutator bars. Check for issues with insulation or brush springs.
-
5. Low Current Draw, Low Shaft Speed:
This could indicate:
- Dirty or corroded connections.
- Damaged wiring.
- Dirty commutator bars.
- All causes from Step 4.
-
6. High Current Draw, High Shaft Speed:
This suggests a short circuit in the field coil. Consider installing a new coil and retesting.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related products
$34.00
$32.00
$34.00
$33.00
$33.00
$34.00








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.