Comprehensive Guide to Track Maintenance and Wear Patterns
Product Overview
This detailed manual offers invaluable insights into the maintenance and wear patterns of track systems used in heavy machinery like dozers and excavators. Understanding these wear patterns is crucial for optimal machine performance and longevity. This guide is packed with actionable advice on diagnosing, managing, and correcting various types of track wear, ensuring you keep your equipment running smoothly.
Key Features
- In-depth Chapter Coverage: The manual covers essential topics like maintenance, engine details, hydraulic systems, electrical schematics, and more.
- Detailed Wear Analysis: Expert insights into different types of track wear, including side wear, inside surface wear, and pin boss top wear.
- Comprehensive Tools Section: Guidance on utilizing special tools for maintenance and repairs.
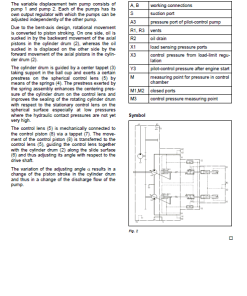
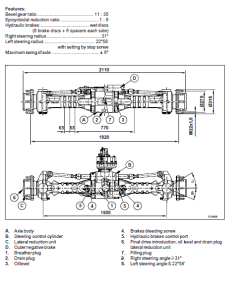
- Visual Aids: Includes electrical and hydraulic schematics to enhance understanding.
Benefits
- Improved Longevity: By following the maintenance guidelines, extend the life of your machinery’s track system.
- Enhanced Performance: Maintain optimal machine performance with regular monitoring and correction of wear patterns.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduce repair costs by addressing potential issues promptly and efficiently.
- Increased Safety: Proper maintenance ensures safer operation, reducing the risk of machine failure.
Usage Recommendations
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections to identify wear early, especially after heavy use in uneven or harsh terrains.
- Address Misalignment: Align tracks properly to prevent accelerated side wear due to misaligned rollers and idlers.
- Manage Track Tension: Regularly adjust track tension to prevent excessive flexing and side loads.
- Utilize Appropriate Track Shoes: Use track shoes of suitable width and grip to minimize unnecessary stress on track components.
Detailed Wear Descriptions
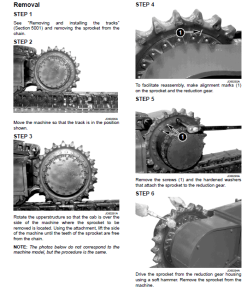
Track Link Wear: As tracks rotate, normal wear results in wavy or scalloped patterns due to contact with idlers, rollers, and carrier rollers. The forward and rearward surfaces tend to wear faster, with central wear being sliding due to less contact area.
Side Wear of the Link Rail: Side wear arises from roller and idler flange contact, exacerbated by side hill operations, turns, and uneven terrain. Misalignment or overly wide track shoes increase this wear, leading to loose track pitches.
Inside Surface Wear of the Link: This occurs when seal failures cause rotating contact between links leading to bushing end wear. Solution: turn pins and bushings, then reseal if link rails aren’t excessively worn.
Pin Boss Top Wear: Results from worn link rail surfaces and roller tread surfaces. Immediate correction is necessary to avoid irreparable damage and machine vibration.
For further reference, view a detailed illustration by clicking: /a>
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.