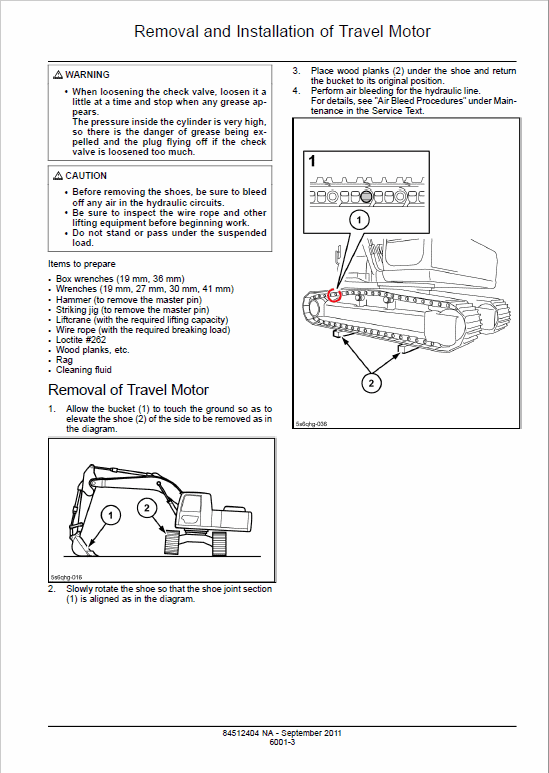
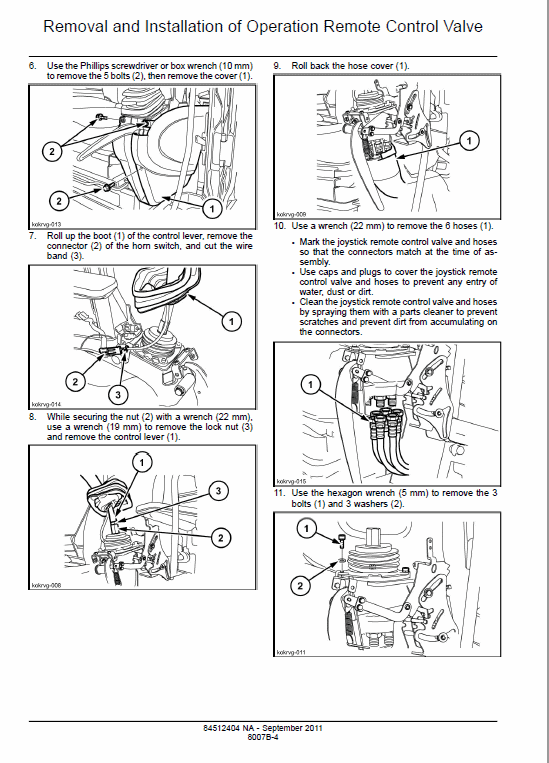
-
×
 Bobcat 2200, 2200s and 2300 Utility Vehicle Service Manual
$32.00
Bobcat 2200, 2200s and 2300 Utility Vehicle Service Manual
$32.00 -
×
 JCB 430ZX Wheeled Loader Shovel Service Manual
$34.00
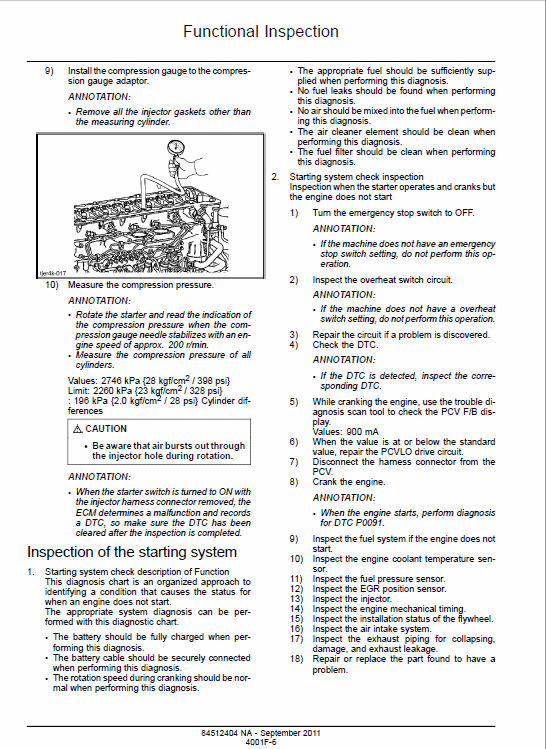
JCB 430ZX Wheeled Loader Shovel Service Manual
$34.00 -
×
 John Deere 862B Series II Scraper Repair Technical Manual (S.N after 818323)
$39.00
John Deere 862B Series II Scraper Repair Technical Manual (S.N after 818323)
$39.00 -
×
 John Deere 862 Scraper Repair Technical Manual (TM1212)
$38.00
John Deere 862 Scraper Repair Technical Manual (TM1212)
$38.00 -
×
 John Deere 710J Backhoe Loader Technical Manual (S.N before - 159769 & 161144 - 172184 )
$56.00
John Deere 710J Backhoe Loader Technical Manual (S.N before - 159769 & 161144 - 172184 )
$56.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 160H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (9JM00001 and up)
$75.00
Caterpillar CAT 160H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (9JM00001 and up)
$75.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140B Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (33C00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 140B Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (33C00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 John Deere 762B Series II Scraper Repair Technical Manual (S.N after 818909)
$39.00
John Deere 762B Series II Scraper Repair Technical Manual (S.N after 818909)
$39.00 -
×
 Bobcat TR38160, TR38160 EVO versaHANDLER Telescopic Service Repair Manual
$36.00
Bobcat TR38160, TR38160 EVO versaHANDLER Telescopic Service Repair Manual
$36.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 12M Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (R9B00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 12M Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (R9B00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Bobcat S630 Skid-Steer Loader Service Manual
$34.00
Bobcat S630 Skid-Steer Loader Service Manual
$34.00 -
×
 JCB 3C, 3CX, 4CX Backhoe Loader Service Repair Manual (960001 to 1625999)
$44.00
JCB 3C, 3CX, 4CX Backhoe Loader Service Repair Manual (960001 to 1625999)
$44.00 -
×
 John Deere 410L Backhoe Loader Technical Manual (S.N C390996 & D390996 - )
$56.00
John Deere 410L Backhoe Loader Technical Manual (S.N C390996 & D390996 - )
$56.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140K 2 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (SZW00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 140K 2 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (SZW00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 160M SERIES 2 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (R9T00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 160M SERIES 2 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (R9T00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT CS-663E, CP-663E Vibratory Compactor Service Repair Manual (ASF00001 and up)
$50.00
Caterpillar CAT CS-663E, CP-663E Vibratory Compactor Service Repair Manual (ASF00001 and up)
$50.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 12H ES Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (2GS00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 12H ES Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (2GS00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 160M 2 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (M9E00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 160M 2 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (M9E00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (82V00001 till 00667)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (82V00001 till 00667)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (13W00425 till 00740)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 140G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (13W00425 till 00740)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 12H NA Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (4XM00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 12H NA Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (4XM00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (82V00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (82V00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 135H NA Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (3YK00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 135H NA Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (3YK00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (72V00001 till 00822)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 140G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (72V00001 till 00822)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (N9400001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 140 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (N9400001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Bobcat TL38.70, TL38.70X versaHANDLER Telescopic Service Repair Manual
$38.00
Bobcat TL38.70, TL38.70X versaHANDLER Telescopic Service Repair Manual
$38.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 160 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5700001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 160 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5700001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 JCB 403 Wheeled Loader Service Manual
$33.00
JCB 403 Wheeled Loader Service Manual
$33.00 -
×
 John Deere XUV 850D M-Gator Utility Vehicle Technical Manual (TM1737)
$39.00
John Deere XUV 850D M-Gator Utility Vehicle Technical Manual (TM1737)
$39.00 -
×
 John Deere 410E Backhoe Loader Repair Technical Manual
$52.00
John Deere 410E Backhoe Loader Repair Technical Manual
$52.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140H NA Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (2ZK00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 140H NA Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (2ZK00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 160M3 AWD Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (N9K00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 160M3 AWD Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (N9K00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 John Deere 315SJ Backhoe Loader Manual (S.N after BE315SJ300869 & T0315SJ178876 - )
$54.00
John Deere 315SJ Backhoe Loader Manual (S.N after BE315SJ300869 & T0315SJ178876 - )
$54.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5400001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 140 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5400001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 John Deere 315SK Backhoe Loader Repair Technical Manual (S.N after C229820 & D219607 - )
$56.00
John Deere 315SK Backhoe Loader Repair Technical Manual (S.N after C229820 & D219607 - )
$56.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (CAF00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (CAF00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 150 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (ENJ00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 150 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (ENJ00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 16 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (EN500001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 16 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (EN500001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 160M Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B9T00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 160M Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B9T00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (Y9D00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (Y9D00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (10R00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (10R00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 John Deere 500C Backhoe Loader Repair Technical Manual (TM1038)
$38.00
John Deere 500C Backhoe Loader Repair Technical Manual (TM1038)
$38.00 -
×
 Bobcat T36.120SL, T36.120SLRB versaHANDLER Telescopic Service Repair Manual
$38.00
Bobcat T36.120SL, T36.120SLRB versaHANDLER Telescopic Service Repair Manual
$38.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 130G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (7GB00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 130G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (7GB00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 150 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5500001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 150 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5500001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140 GC Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (W9300001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 140 GC Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (W9300001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (9TN00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 140H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (9TN00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 John Deere 710L Backhoe Loader Repair Technical Manual (S.N after F294268 - F390995)
$60.00
John Deere 710L Backhoe Loader Repair Technical Manual (S.N after F294268 - F390995)
$60.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 14 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (NN400001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 14 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (NN400001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (1LK00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (1LK00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (ENF00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 140 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (ENF00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (11W01019 till 11W01250)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (11W01019 till 11W01250)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (13W00741 till 00992)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 140G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (13W00741 till 00992)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 143H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (APN00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 143H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (APN00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140B Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (61S00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 140B Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (61S00001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 JCB Groundhog 4x4 Utility Vehicle Service Manual
$31.00
JCB Groundhog 4x4 Utility Vehicle Service Manual
$31.00 -
×
 John Deere 762A Scraper Repair Technical Manual (TM1225)
$38.00
John Deere 762A Scraper Repair Technical Manual (TM1225)
$38.00 -
×
 JCB Vibromax 355, 365, 455, 465 Tandum Roller Service Manual
$26.70
JCB Vibromax 355, 365, 455, 465 Tandum Roller Service Manual
$26.70 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (ALZ00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 120H Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (ALZ00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 JCB Vibromax VM106 Single Drum Roller Service Manual
$26.00
JCB Vibromax VM106 Single Drum Roller Service Manual
$26.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (82V00668 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (82V00668 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 150 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5600001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 150 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5600001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 John Deere 710J Backhoe Loader Technical Manual (S.N 159770 - 161143 and after 172185 - )
$54.00
John Deere 710J Backhoe Loader Technical Manual (S.N 159770 - 161143 and after 172185 - )
$54.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 12G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (61M02629 till 07710)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 12G Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (61M02629 till 07710)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 160 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5900001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 160 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B5900001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 140M Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B9D00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 140M Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B9D00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 12H NA Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (2WR00001 and up)
$70.00
Caterpillar CAT 12H NA Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (2WR00001 and up)
$70.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 14L Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B9400001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 14L Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (B9400001 and up)
$80.00 -
×
 John Deere 110 Tractor Loader Backhoe Technical Manual (TM1987)
$38.00
John Deere 110 Tractor Loader Backhoe Technical Manual (TM1987)
$38.00 -
×
 JCB Groundhog 6x4 Utility Vehicle Service Manual
$30.00
JCB Groundhog 6x4 Utility Vehicle Service Manual
$30.00 -
×
 Bobcat BL570, BL575 Loader Service Repair Manual
$38.00
Bobcat BL570, BL575 Loader Service Repair Manual
$38.00 -
×
 Caterpillar CAT 120 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (Y9A00001 and up)
$80.00
Caterpillar CAT 120 Motor Grader Service Repair Manual (Y9A00001 and up)
$80.00
Case CX470C Crawler Excavator Service Manual
$35.00
Enhance your understanding of the New Holland CX470C Excavator with this comprehensive Service Manual, spanning 1822 pages. This manual provides detailed insights and specifications essential for maintenance and operation.
Brand: New Holland
Model: CX470C
Type: Excavator
Manual: Service Manual
Publication Number: 84512404 (Oct 2011)
Language: English
Format: PDF
Product Manual Overview
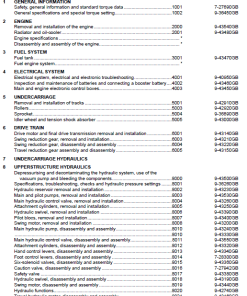
Table of Contents
- General Information
- Engine
- Fuel System
- Electrical System
- Undercarriage
- Drive Train
- Upper Structure Hydraulics
- Upper Structure
- Hydraulic Schematics
- Electrical Schematics
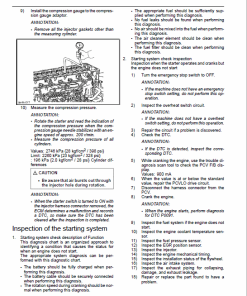
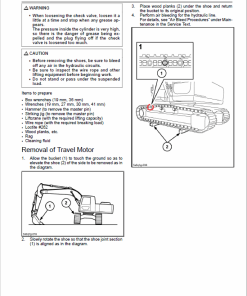
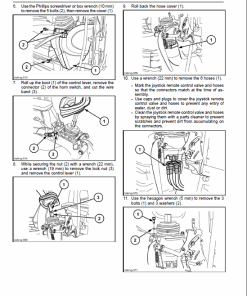
Engine Stalling Diagnostics
Diagnosing engine stalling involves an initial examination and troubleshooting of symptoms where the engine cranks but takes time to start, or where it starts but soon stops operating. Hereu2019s a detailed guide to help troubleshoot these issues:
Preliminary Inspection
- Perform a functional inspection and OBD system check.
- Assess for excessive loads on the machine side.
- Ensure proper operation of the ECM and monitor.
- To diagnose CKP sensor abnormalities, crank the engine for a minimum of 14 seconds at 60 r/min.
- Conduct a DTC check, especially considering CKP sensor failures at low revolutions may not always be detected.
- In the event of sporadic failures, increase engine revolutions to No Load Max to verify DTC detections related to the CKP sensor.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection can be crucial for resolving symptoms efficiently. It may prevent the need for extensive further inspections.
- Check for poor connections at connectors, especially those linked to CKP and CMP sensors.
- Ensure all wiring is properly connected and tightened, and that the ECM ground is clean and correctly positioned.
- Inspect pipes and hoses for cracks, twists, leaks or blockages, particularly in fuel, air, and oil systems.
- Examine the fuel system for damage or leaks, and check the layout of the fuel filter, pre-filter, and electromagnetic pump to prevent air stagnation.
- Verify that the Isuzu genuine pre-filter is positioned to avoid air stagnant issues, noting that it lacks an air bleeding plug.
- Identify any abnormalities in the intake and exhaust system components.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related products
$34.00
$34.00
$34.00
$34.00
$34.00









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.